Page 180 - Science Course 1 (Book 1)
P. 180
Matter: Gas Behavior Mo5-L4a: How are Boyle's Law and
Charles Law Related?
Lesson 4
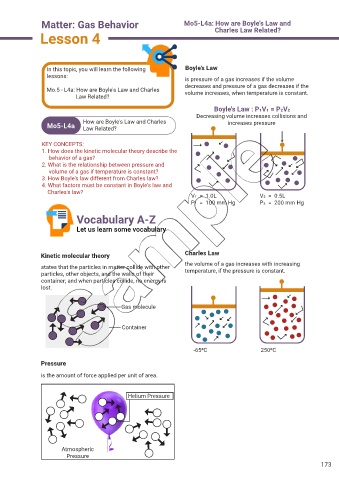
In this topic, you will learn the following Boyle’s Law
lessons: is pressure of a gas increases if the volume
decreases and pressure of a gas decreases if the
Mo.5 - L4a: How are Boyle's Law and Charles volume increases, when temperature is constant.
Law Related?
Boyle's Law : P1V1 = P2V2
Decreasing volume increases collisions and
How are Boyle's Law and Charles increases pressure
Mo5-L4a Law Related?
KEY CONCEPTS:
1. How does the kinetic molecular theory describe the
behavior of a gas?
2. What is the relationship between pressure and
volume of a gas if temperature is constant?
3. How Boyle's law different from Charles law?
4. What factors must be constant in Boyle's law and
Charles's law?
V1 = 1.0L V2 = 0.5L
P1 = 100 mm Hg P2 = 200 mm Hg
Vocabulary A-Z
Let us learn some vocabulary
Kinetic molecular theory Charles Law
states that the particles in matter collide with other the volume of a gas increases with increasing
temperature, if the pressure is constant.
particles, other objects, and the walls of their
container; and when particles collide, no energy is
lost.
Gas molecule
Container
-650C 2500C
Pressure
is the amount of force applied per unit of area.
Helium Pressure
Atmospheric
Pressure
173