Page 220 - Math Course 3 (Book 2)
P. 220
Probability Simulations
Mo. 12
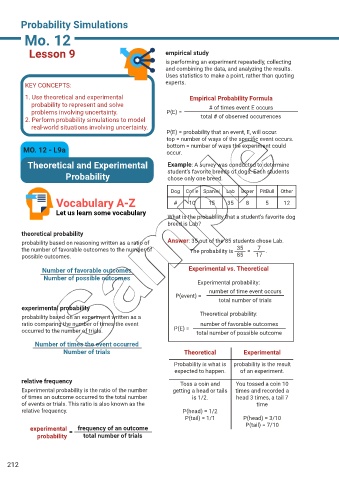
Lesson 9 empirical study
is performing an experiment repeatedly, collecting
and combining the data, and analyzing the results.
Uses statistics to make a point, rather than quoting
KEY CONCEPTS: experts.
1. Use theoretical and experimental Empirical Probability Formula
probability to represent and solve # of times event E occurs
problems involving uncertainty. P(E) =
2. Perform probability simulations to model total # of observed occurrences
real-world situations involving uncertainty.
P(E) = probability that an event, E, will occur.
top = number of ways of the specific event occurs.
MO. 12 - L9a bottom = number of ways the experiment could
occur.
Theoretical and Experimental Example: A survey was conducted to determine
Probability student’s favorite breeds of dogs. Each students
chose only one breed.
Dog Collie Spaniel Lab Boxer PitBull Other
Vocabulary A-Z # 10 15 35 8 5 12
Let us learn some vocabulary
What is the probability that a student’s favorite dog
breed is Lab?
theoretical probability
probability based on reasoning written as a ratio of Answer: 35 out of the 85 students chose Lab.
7
35
the number of favorable outcomes to the number of The probability is = .
possible outcomes. 85 17
Number of favorable outcomes Experimental vs. Theoretical
Number of possible outcomes
Experimental probability:
number of time event occurs
P(event) =
total number of trials
experimental probability
probability based on an experiment written as a Theoretical probability:
ratio comparing the number of times the event number of favorable outcomes
occurred to the number of trials. P(E) = total number of possible outcome
Number of times the event occurred
Number of trials Theoretical Experimental
Probability is what is probability is the result
expected to happen. of an experiment.
relative frequency Toss a coin and You tossed a coin 10
Experimental probability is the ratio of the number getting a head or tails times and recorded a
of times an outcome occurred to the total number is 1/2. head 3 times, a tail 7
of events or trials. This ratio is also known as the time
relative frequency. P(head) = 1/2
P(tail) = 1/1 P(head) = 3/10
experimental = frequency of an outcome P(tail) = 7/10
probability total number of trials
212