Page 191 - Science Course 1 (Book 1)
P. 191
Mo6-L1a: How did the Atomic Theory Start?
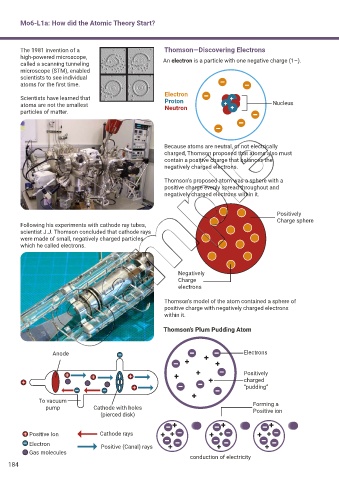
The 1981 invention of a Thomson—Discovering Electrons
high-powered microscope, An electron is a particle with one negative charge (1–).
called a scanning tunneling
microscope (STM), enabled
scientists to see individual
atoms for the first time.
Electron
Scientists have learned that Proton +
atoms are not the smallest Neutron + + Nucleus
particles of matter.
Because atoms are neutral, or not electrically
charged, Thomson proposed that atoms also must
contain a positive charge that balances the
negatively charged electrons.
Thomson’s proposed atom was a sphere with a
positive charge evenly spread throughout and
negatively charged electrons within it.
Positively
Charge sphere
Following his experiments with cathode ray tubes,
scientist J.J. Thomson concluded that cathode rays
were made of small, negatively charged particles
which he called electrons.
Negatively
Charge
electrons
Thomson’s model of the atom contained a sphere of
positive charge with negatively charged electrons
within it.
Thomson’s Plum Pudding Atom
Anode Electrons
Positively
charged
“pudding”
To vacuum Forming a
pump Cathode with holes Positive ion
(pierced disk)
Positive Ion Cathode rays
Electron Positive (Canal) rays
Gas molecules
conduction of electricity
184