Page 155 - Math Course 1 (Book 2)
P. 155
Understanding Histograms
Mo. 11
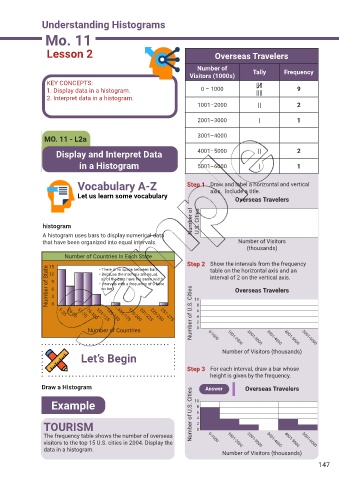
Lesson 2 Overseas Travelers
Number of Tally Frequency
Visitors (1000s)
KEY CONCEPTS: ||||
1. Display data in a histogram. 0 – 1000 |||| 9
2. Interpret data in a histogram.
1001–2000 || 2
2001–3000 | 1
MO. 11 - L2a 3001–4000
Display and Interpret Data 4001–5000 || 2
in a Histogram 5001–6000 | 1
Vocabulary A-Z Step 1 Draw and label a horizontal and vertical
Let us learn some vocabulary axis. Include a title.
Overseas Travelers
Number of U.S. Cities
histogram
A histogram uses bars to display numerical data
that have been organized into equal intervals. Number of Visitors
(thousands)
Number of Countries In Each State
Step 2 Show the intervals from the frequency
15
Number of State 9 6 3 0 all of the bars have the same width. 10 8 interval of 2 on the vertical axis.
• There is no space between bars
table on the horizontal axis and an
12
• Because the intervals are equal,
• Intervals with a frequency of 0 have
no bar.
Overseas Travelers
1-25
51-75
26-50
76-100
226-250
101-125
151-175
126-150
176-200
Number of Countries 201-225 251-275 Number of U.S. Cities 6 4 2 0 0-1000 1001-2000 2001-3000 3001-4000 4001-5000 5001-6000
Number of Visitors (thousands)
Let’s Begin
Step 3 For each interval, draw a bar whose
height is given by the frequency.
Draw a Histogram Answer Overseas Travelers
Example Number of U.S. Cities 10 8 6
TOURISM 4 2 0
The frequency table shows the number of overseas 0-1000
visitors to the top 15 U.S. cities in 2004. Display the 1001-2000 2001-3000 3001-4000 4001-5000 5001-6000
data in a histogram.
Number of Visitors (thousands)
147